Motion Analysis Insights - June 2025

When Technology Meets Rehabilitation:
The use of BTS NIRVANA
The Role of Virtual and Augmented Reality in Neurological Rehabilitation
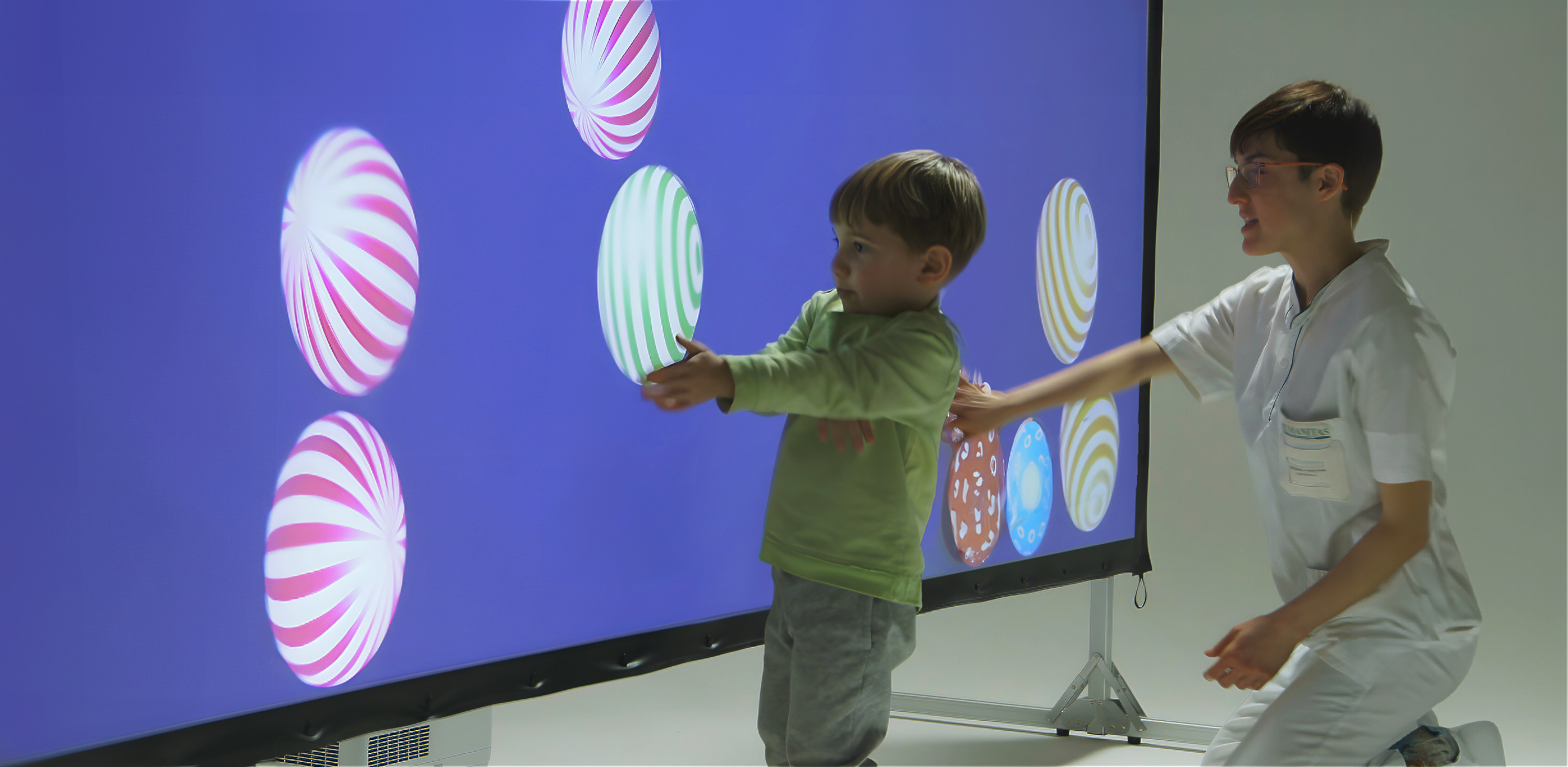
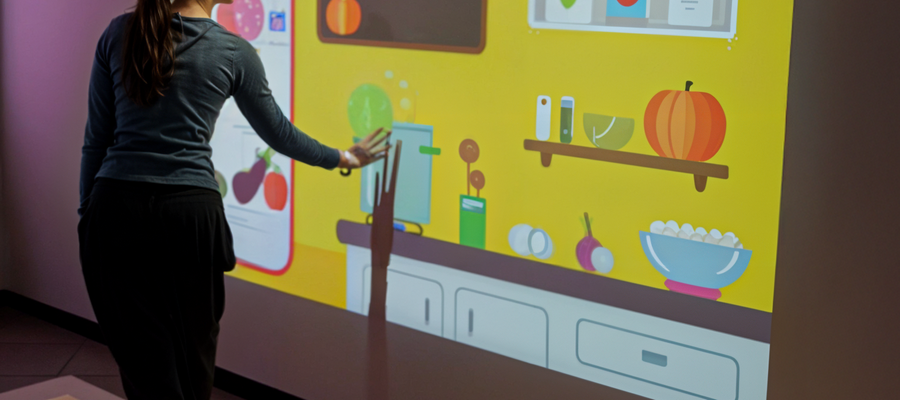
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are emerging as powerful tools in neurological rehabilitation, offering innovative ways to support motor and cognitive recovery. By creating immersive or semi-immersive environments, these technologies simulate real-life scenarios, allowing patients to engage in controlled, interactive, and motivating therapeutic tasks.
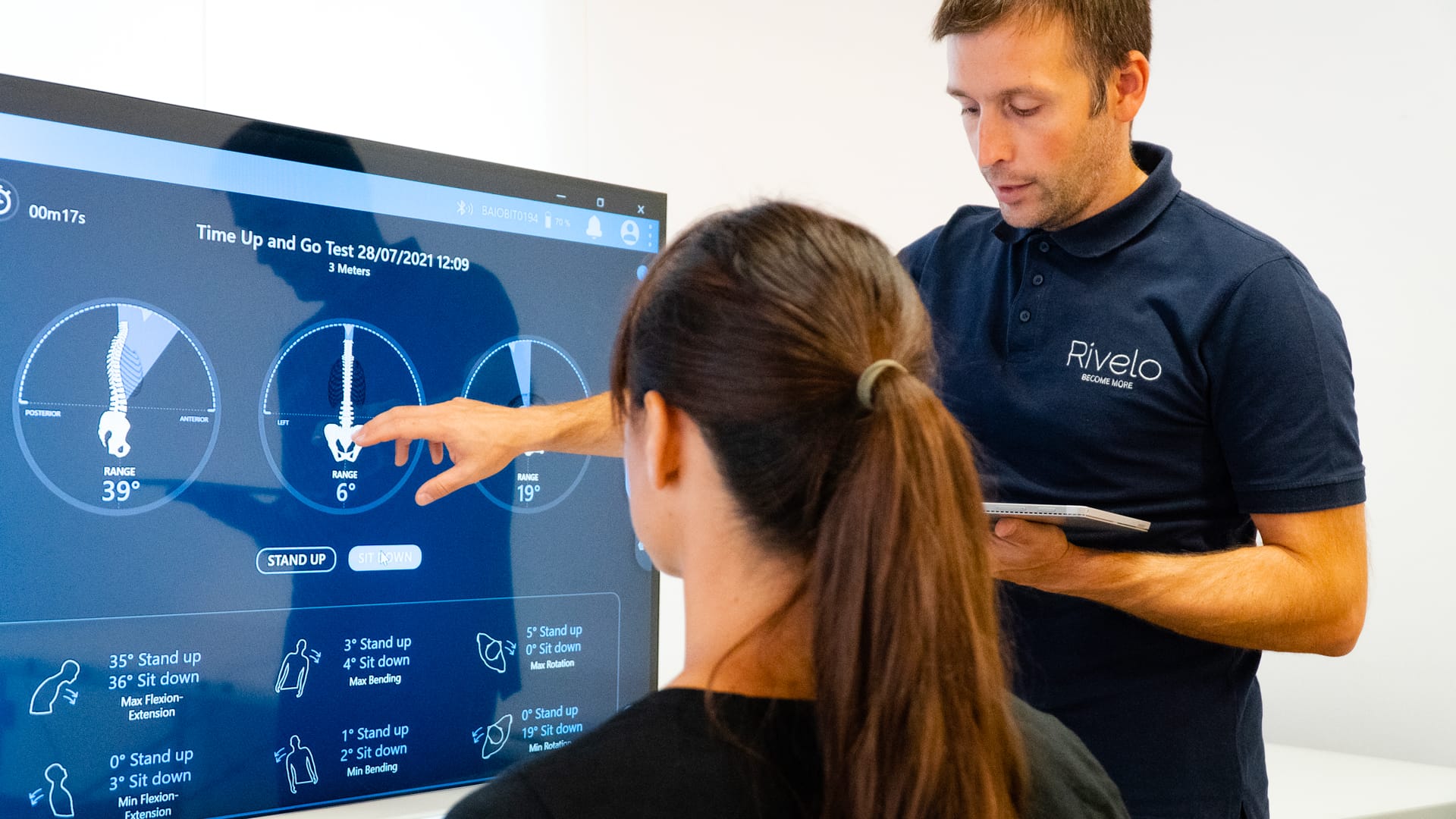
For neurological patients, VR and AR promote neuroplasticity through repetitive, goal-oriented movements and cognitive exercises. Systems like BTS Nirvana provide real-time visual feedback, helping patients understand their performance and track progress.
Studies show that VR and AR therapies can improve limb function, balance, coordination, and even emotional well-being. These tools also boost patient motivation and adherence by turning therapy into a more game-like and rewarding experience.
New and upcoming features in BTS Nirvana:
Precision, Tracking, and Integration
BTS Nirvana continues to evolve with new features aimed at improving accuracy, usability, and clinical impact in neurorehabilitation.
🔹 Dual-Sensor Configuration
The latest update allows the use of two sensors per setup, reducing blind spots and capturing movement from multiple angles. This enables smoother, more natural interaction—especially helpful for patients with mobility or coordination difficulties.
🔹 Markerless Skeleton Tracking
Real-time motion recognition now includes a markerless skeletal model, allowing the system to differentiate between limbs. This supports more precise feedback and analysis of asymmetries, improving both motor and cognitive rehab outcomes.
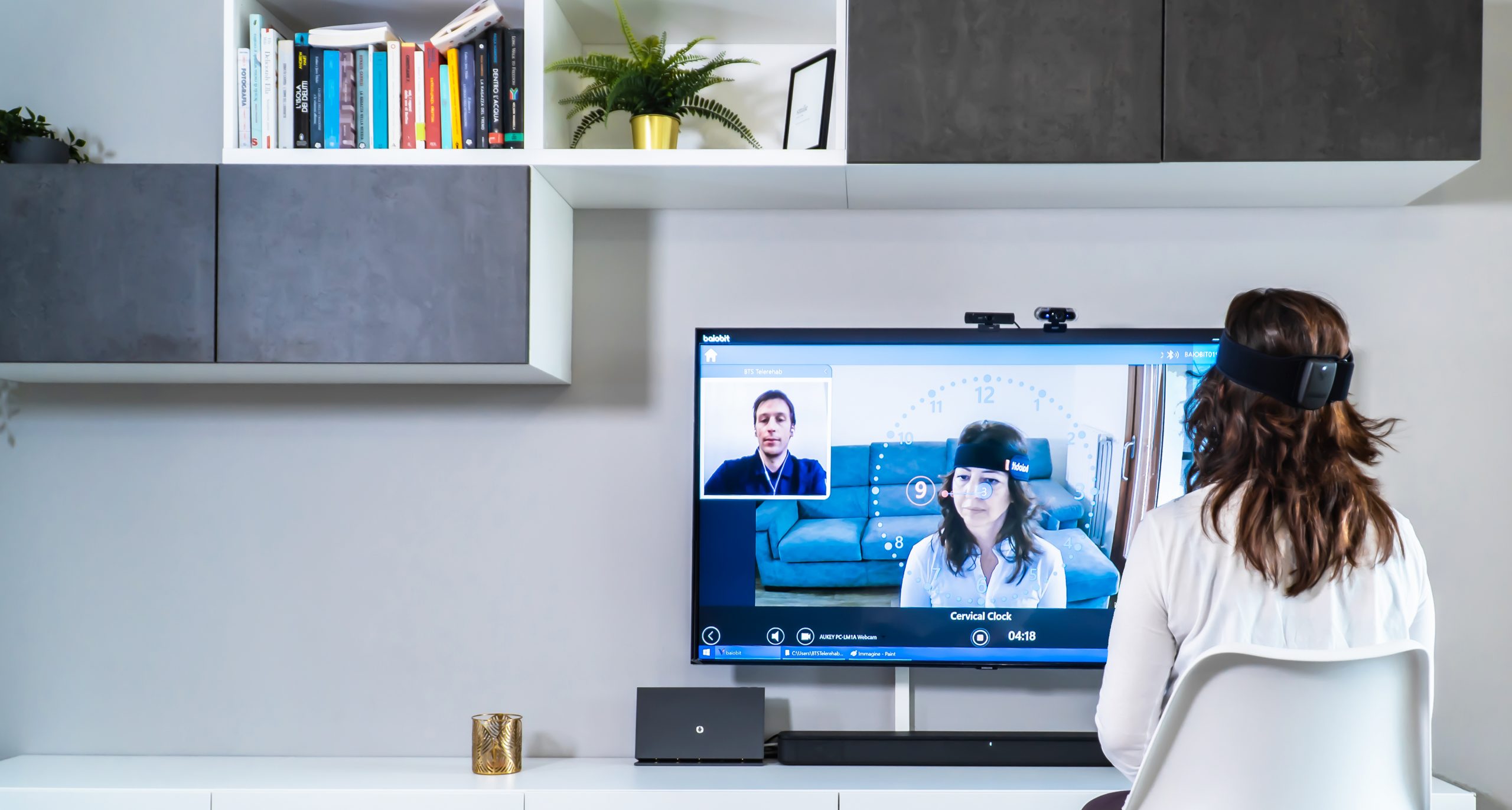
🔹 Upcoming Inertial Sensor Integration
Soon, Nirvana will integrate with BTS inertial sensors for enhanced kinematic data. This will streamline assessments and offer deeper insight into movement quality—making therapy more personalized and evidence-based.
These upgrades reinforce BTS Nirvana’s position as a leading solution in virtual reality-based rehabilitation, combining immersive interaction with precise, real-time data to support effective therapy and evidence-based clinical decision-making.
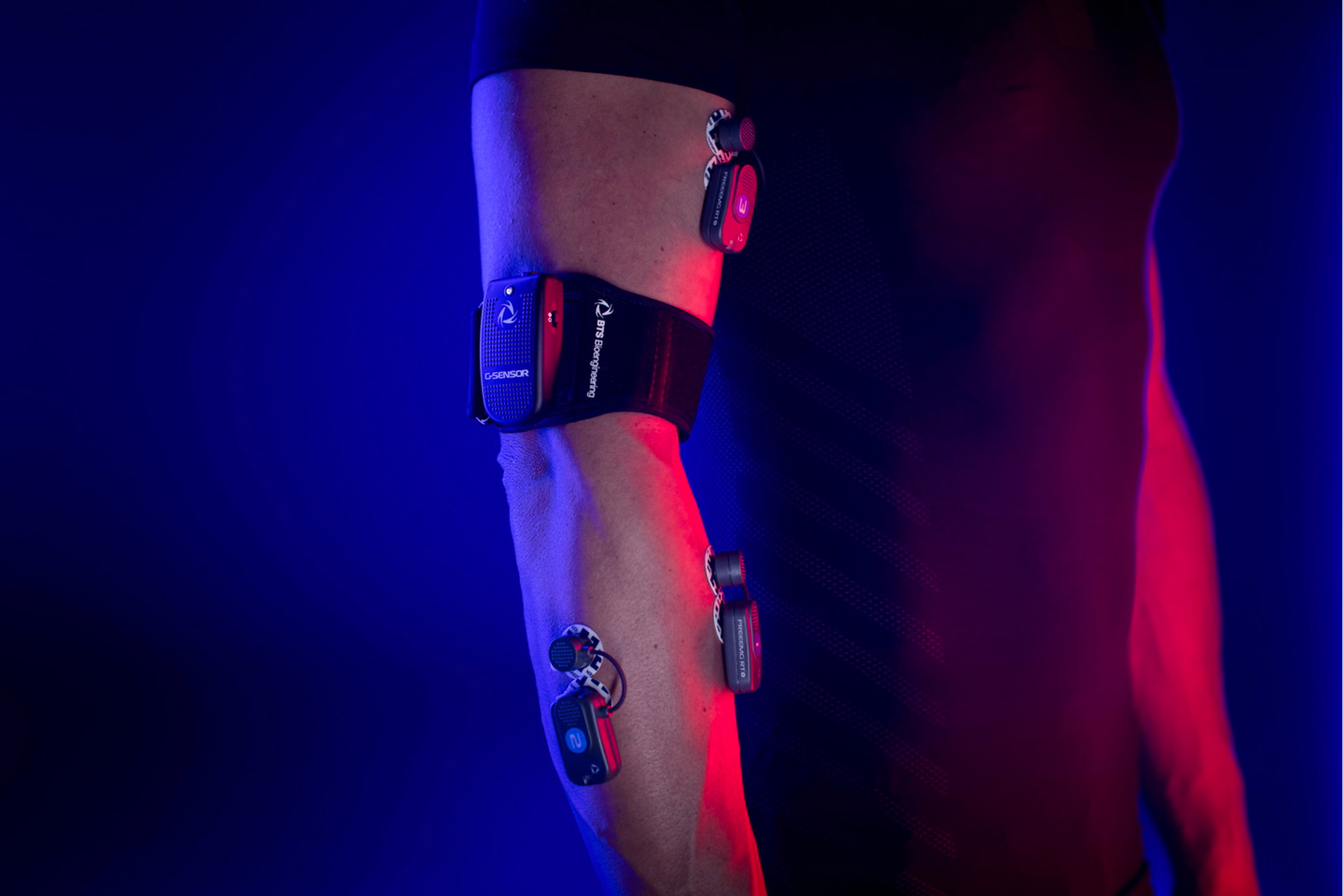
This study explored the effects of repeated drop jump (DJ) training at different heights on countermovement jump (CMJ) performance in male athletes. Using the BTS SMART-DX infrared motion capture system and BTS P-6000 force plates, researchers measured key performance metrics such as jump height, contact time, reactive strength index, and average rate of force development. The findings highlight that DJ training at 50 cm height effectively enhances stretch-shortening cycle function, neuromuscular adaptability, and jump performance, but only when training volume is kept at or below 200 jumps. Exceeding this threshold leads to fatigue, reduced CMJ performance, and increased injury risk. Therefore, the study recommends limiting high-intensity DJ training at 50 cm to 200 repetitions to maximize benefits while minimizing fatigue and injury.
He L, Li YG, Wu C, Yao S, Su Y, Ma GD, Wang IL. The Influence of Repeated Drop Jump Training on Countermovement Jump Performance. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2022 Feb 21;2022:9609588. doi: 10.1155/2022/9609588. PMID: 35237347; PMCID: PMC8885253.
 The University of Alabama
The University of Alabama
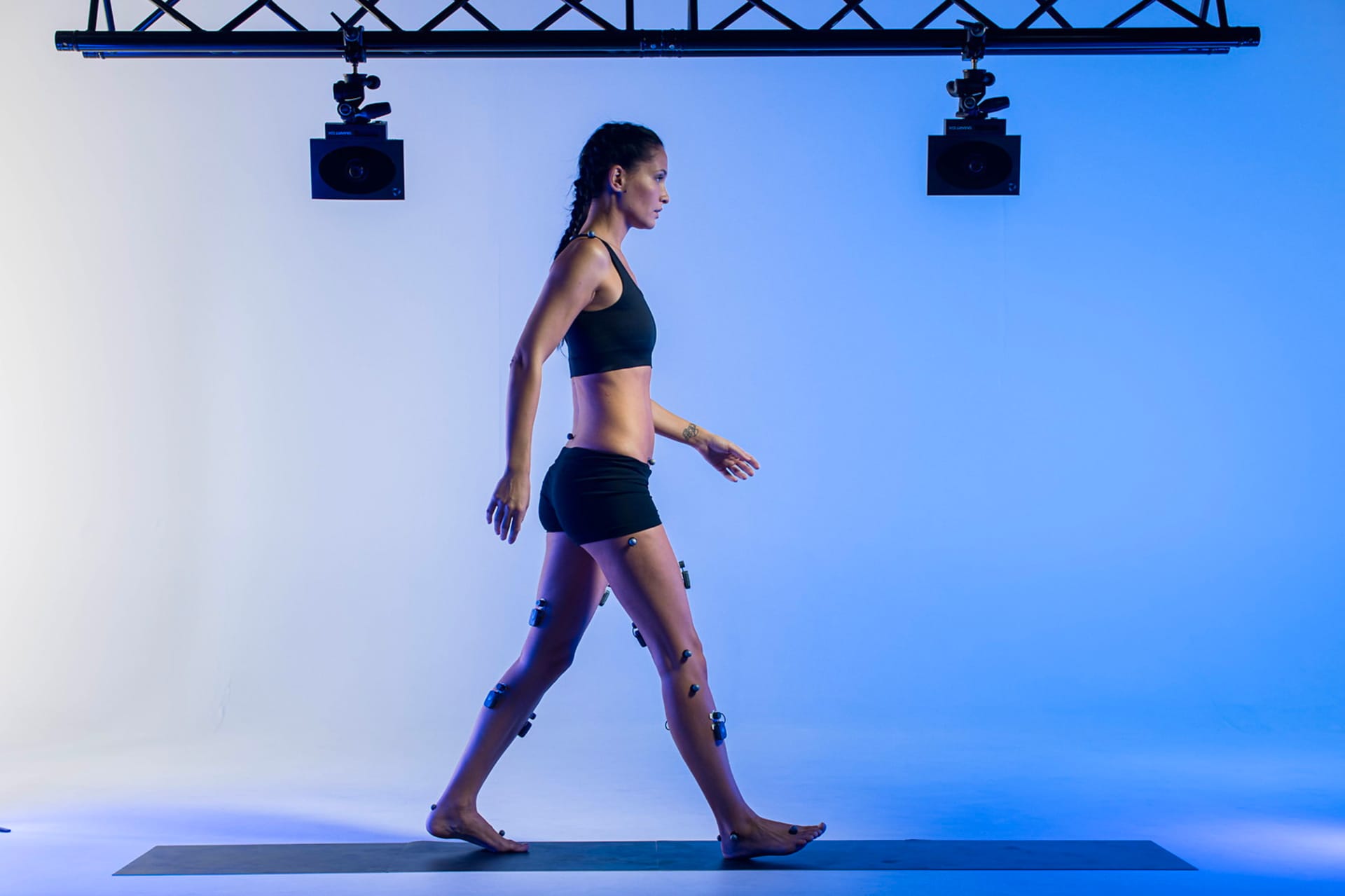
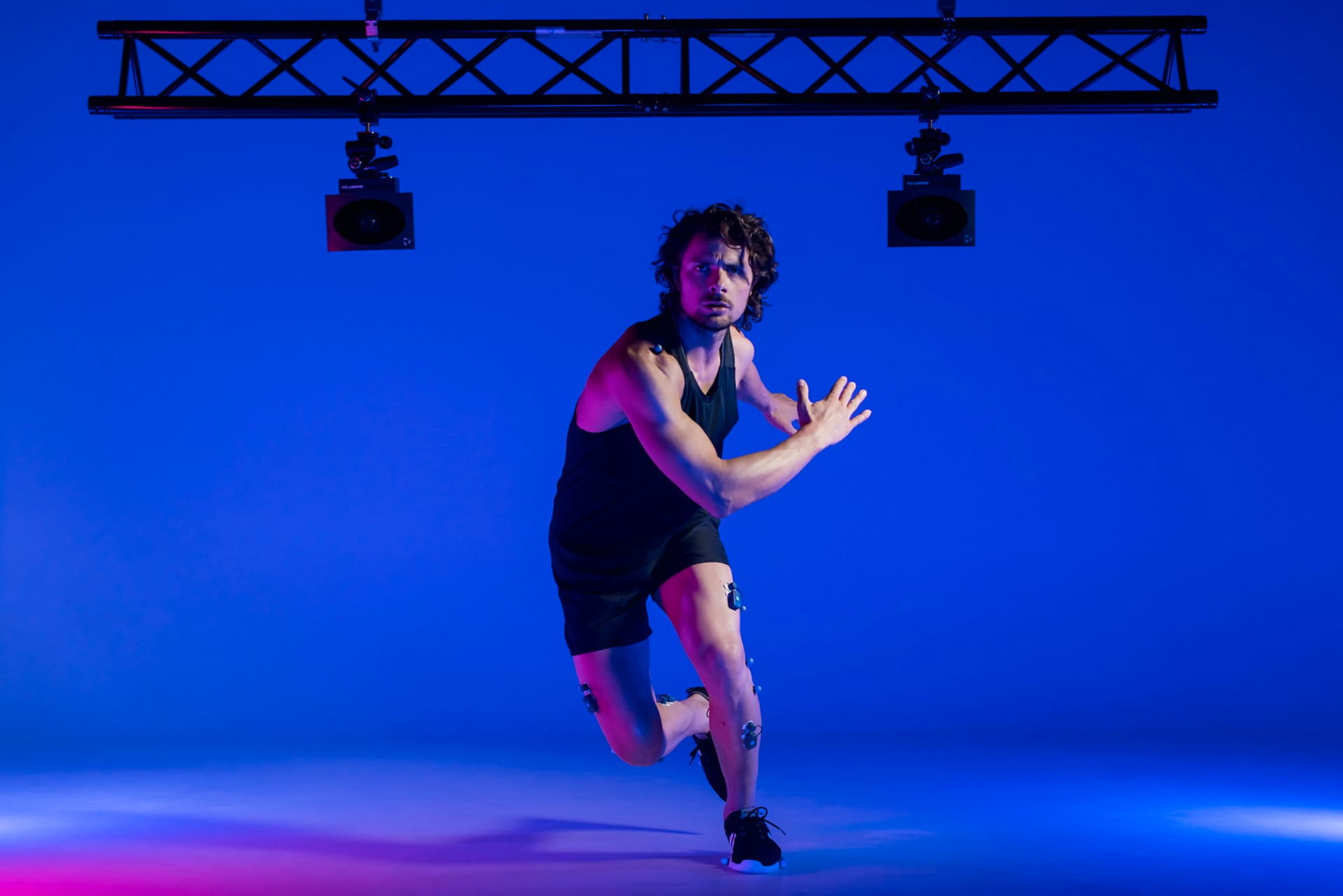
The University of Alabama has significantly advanced its sports science capabilities by establishing a state-of-the-art biomechanics facility, integrating BTS Bioengineering’s SPORTLAB system. This initiative aims to bridge academic research with athletic performance enhancement, providing a comprehensive platform for analyzing and improving athlete biomechanics.
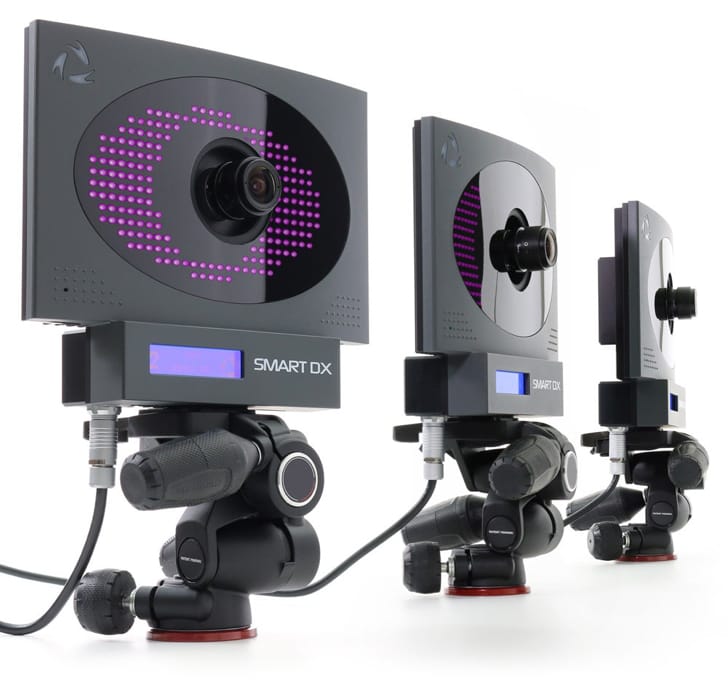
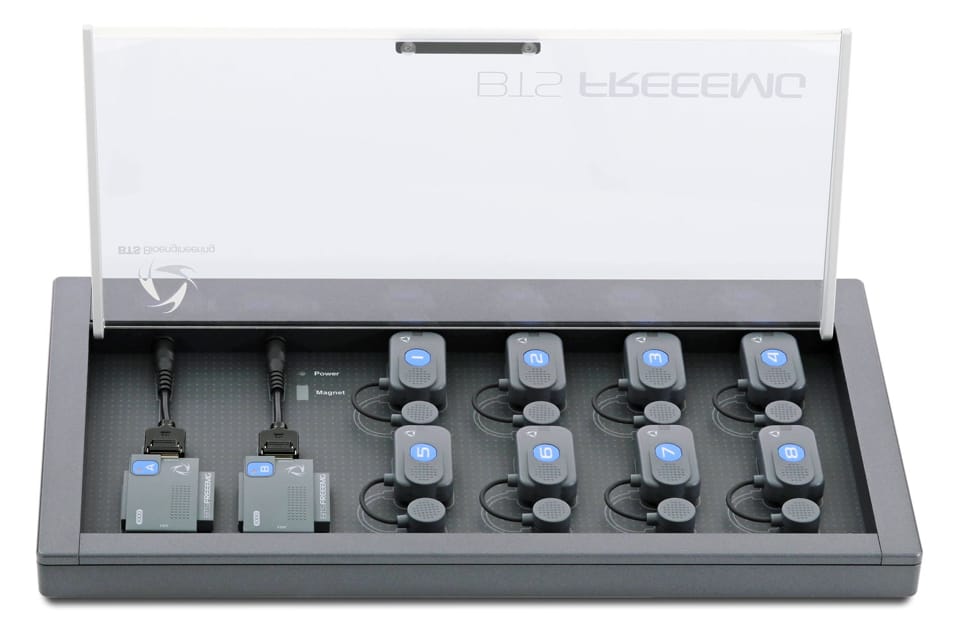
Central to this facility is the integration of advanced technologies, including the SMART-DX EVO motion capture system, FREEEMG for electromyography, and 3D P-6000 force plates. These tools enable synchronized collection of kinematic, dynamic, and muscular activity data, allowing for detailed analysis of athletic movements. Such integration facilitates the development of optimized training protocols, injury prevention strategies, and rehabilitation programs.